Smart bulbs can be more energy efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, especially when paired with smart features like scheduling and dimming. However, their efficiency depends on the bulb type, usage patterns, and smart home setup. By choosing the right bulbs and using automation wisely, you can reduce energy consumption and lower your electricity bill.
Key Takeaways
- LED Technology is Key: Most smart bulbs use LED technology, which is inherently more energy-efficient than incandescent or halogen bulbs, using up to 90% less energy.
- Smart Features Save Energy: Features like motion detection, scheduling, and dimming help reduce unnecessary usage and optimize energy use throughout the day.
- Energy Usage Varies by Model: Not all smart bulbs are equal—efficiency depends on the bulb’s wattage, lumens output, and whether it includes energy-saving modes.
- Dimming Saves More Energy: Dimming smart bulbs can reduce energy consumption by up to 50%, making them even more efficient when used with dimmer switches.
- Compatibility Matters: Using smart bulbs with compatible hubs or apps ensures full functionality, including energy monitoring and automation, which supports efficiency.
- Lifespan Reduces Waste: Smart bulbs last 25,000 to 50,000 hours, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering long-term energy and resource use.
- Cost vs. Savings: While smart bulbs cost more upfront, their energy savings and automation features often pay off over time, especially in high-usage areas.
📑 Table of Contents
- Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient?
- How Smart Bulbs Work and Why They’re Different
- Energy Efficiency Compared: Smart vs. Traditional Bulbs
- The Role of Smart Features in Energy Savings
- Energy Usage: What to Expect from Smart Bulbs
- Cost vs. Long-Term Savings
- Tips for Maximizing Energy Efficiency with Smart Bulbs
- Environmental Impact of Smart Bulbs
- Common Misconceptions About Smart Bulbs
- Conclusion: Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient?
Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient?
Imagine turning off the lights in a room you’re leaving—without even thinking about it. That’s the magic of smart bulbs. They’re more than just lights you control with your phone or voice. They’re part of a smarter, more efficient home. But here’s the real question: Are smart bulbs actually more energy efficient than traditional bulbs? The short answer? Yes—but with a few important caveats.
Smart bulbs, especially those built on LED technology, use significantly less energy than old incandescent bulbs. But their real energy-saving power comes from the smart features they offer: scheduling, dimming, motion detection, and remote control. When used wisely, these features help you avoid wasting electricity. Still, not all smart bulbs are created equal. Some use more power than others, and not every homeowner uses them in the most efficient way. So, let’s dig into what makes smart bulbs efficient, how they compare to traditional lighting, and how you can make the most of them.
How Smart Bulbs Work and Why They’re Different
Smart bulbs are essentially regular bulbs with added technology. At their core, they still produce light—but they’re connected to Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee, allowing you to control them from your smartphone, voice assistant, or smart home hub. But what makes them “smart” is the software and sensors that come with them.

Visual guide about Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient
Image source: pluspng.com
The Technology Behind Smart Lighting
Most smart bulbs use LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology. LEDs are far more energy-efficient than older lighting types like incandescent or halogen bulbs. They convert up to 90% of energy into light, while incandescent bulbs waste most of their energy as heat. This efficiency is built into the bulb itself—no smart features required.
But here’s where the “smart” part comes in: these bulbs often include built-in controls for brightness, color, and scheduling. Some even have motion sensors or daylight harvesting, which automatically adjust lighting based on room occupancy or natural light levels. All of these features help you use less energy—without sacrificing comfort or convenience.
Examples of Smart Bulb Technology
- Philips Hue: One of the most popular smart bulb brands, Hue bulbs use Zigbee technology and work with Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple HomeKit. They offer dimming, color changing, and energy monitoring.
- TP-Link Kasa Smart Bulbs: These bulbs are affordable and easy to set up. They include scheduling, dimming, and remote access, and use less power than traditional bulbs.
- LIFX Bulbs: These bulbs don’t require a hub and use Wi-Fi directly. They support voice control and color customization, and some models include energy usage tracking.
Each of these examples shows how smart bulbs go beyond basic lighting. They’re designed to integrate into your daily routine, making it easier to use light only when and where it’s needed.
Energy Efficiency Compared: Smart vs. Traditional Bulbs
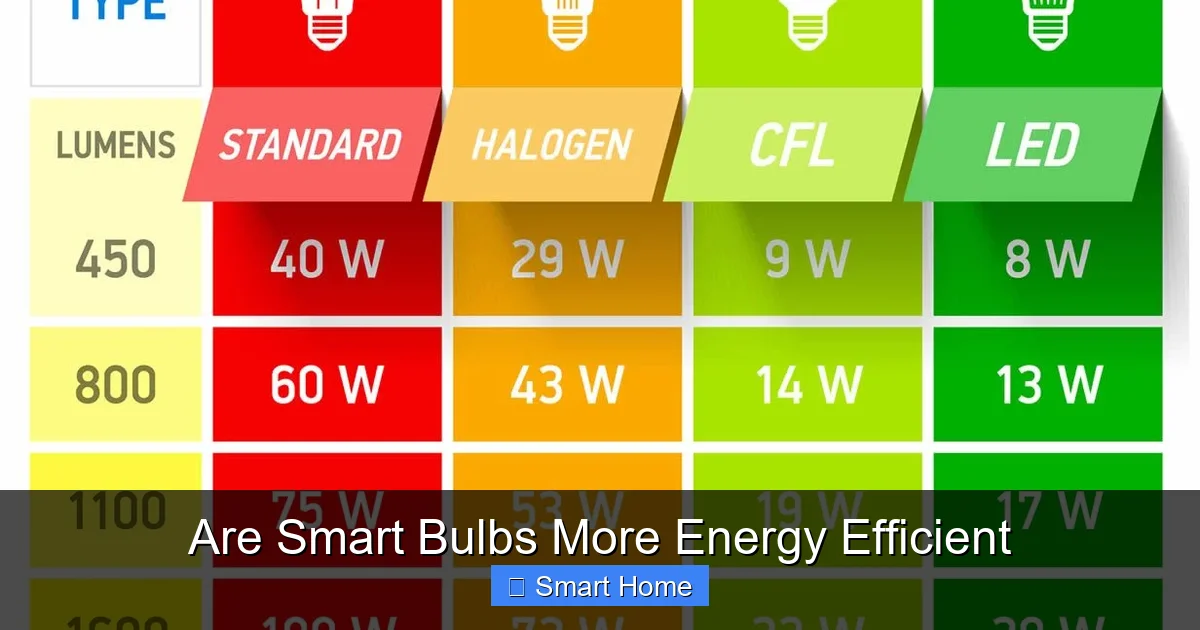
To understand if smart bulbs are more energy efficient, we need to compare them to the bulbs they’re replacing. Let’s look at three common types: incandescent, halogen, and CFL (compact fluorescent lamp).
Visual guide about Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient
Image source: i.pinimg.com
Incandescent Bulbs: The Least Efficient
Incandescent bulbs are the least energy-efficient option. They use about 90% of their energy to produce heat, not light. A 60-watt incandescent bulb produces only about 800 lumens—roughly the same as a 9-watt LED bulb. That means replacing one incandescent bulb with a smart LED bulb could save you up to 85% on lighting energy costs.
For example, if you leave a 60-watt bulb on for 5 hours a day, that’s 300 watts per day. Switching to a 9-watt smart bulb reduces that to just 45 watts—saving 255 watts daily, or about 92,775 watts (or 92.8 kWh) per year. At an average electricity rate of $0.12 per kWh, that’s a savings of over $11 per year just from one bulb.
Halogen Bulbs: Slightly Better, Still Inefficient
Halogen bulbs are a bit more efficient than incandescent bulbs—using about 25% to 30% less energy for the same light output. However, they still generate a lot of heat and have a short lifespan. A smart LED bulb will still outperform a halogen in both energy use and longevity.
CFL Bulbs: Better Than Incandescents, But Outdated
CFL bulbs use about 25% less energy than incandescent bulbs and last much longer. However, they contain small amounts of mercury and are less flexible in terms of dimming and color control. Smart LED bulbs offer better performance, greater control, and no environmental concerns.
Smart LED Bulbs: The Most Efficient Option
Smart LED bulbs combine the energy efficiency of LEDs with the convenience of automation. They use 75% to 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs and can be programmed to turn off when not needed. When paired with smart home systems, they can learn your habits and adjust lighting automatically—further reducing waste.
The Role of Smart Features in Energy Savings
Here’s where smart bulbs really shine: their ability to save energy through intelligent features. It’s not just about using less wattage—it’s about using light more wisely.

Visual guide about Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient
Image source: cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net
Scheduling and Automation
One of the easiest ways to save energy is by scheduling your lights. For example, you can set your bedroom light to turn on at 6:30 a.m. and off at 11:00 p.m. This prevents lights from being left on overnight or in empty rooms. Many smart bulbs allow you to create routines based on sunrise, sunset, or your calendar.
Example: A family living in a suburban home uses smart bulbs in the living room and kitchen. They set a routine to turn off all lights at 11:00 p.m. and turn them back on at 6:00 a.m. This simple change saves about 150 kWh per month—enough to power a laptop for over a year.
Motion Sensors and Occupancy Detection
Some smart bulbs come with built-in motion sensors or work with smart plugs that detect movement. When no one is in the room, the lights automatically dim or turn off. This is especially useful in hallways, closets, and bathrooms.
Tip: Place smart bulbs in high-traffic areas with motion sensors to cut down on wasted light. For instance, a smart bulb in a basement stairwell can turn on only when someone walks by, saving energy compared to leaving a light on all day.
Dimming and Brightness Control
Dimming smart bulbs can reduce energy use by up to 50%. Lower brightness means less electricity consumed—even with LED technology. Most smart bulbs work with dimmer switches, allowing you to adjust light levels based on the time of day or activity.
Example: A homeowner uses smart bulbs in their dining room. During dinner, they dim the lights to 50%. During a movie night, they drop it to 20%. This not only saves energy but also creates the right mood—without overworking the bulb or the power grid.
Geofencing and Location-Based Automation
Geofencing uses your phone’s location to control your lights. When you leave the house, the lights turn off. When you return, they turn on. This prevents lights from being left on when no one is home.
Real-World Impact: A study by the U.S. Department of Energy found that homes with geofencing-based lighting saved an average of 10% on their annual electricity bill. That’s because lights are only on when needed—no more forgotten switches or empty rooms lit all night.
Energy Usage: What to Expect from Smart Bulbs
Not all smart bulbs use the same amount of energy. The actual wattage depends on the bulb’s design, brightness (measured in lumens), and features. Let’s compare a few common types:
- Smart LED Bulb (60W equivalent): Uses 9–12 watts, produces 800 lumens, lasts 25,000+ hours.
- Smart LED Bulb (100W equivalent): Uses 14–18 watts, produces 1600 lumens, lasts 25,000+ hours.
- Smart Color Bulb: Uses 10–15 watts, offers full-color control, but may consume slightly more power due to RGB LEDs.
Even though color-changing smart bulbs use a bit more energy, they’re still far more efficient than incandescent bulbs. And because they’re used in moderation (e.g., for ambiance), the extra energy use is minimal compared to the savings from automation.
Energy Monitoring and Reporting
Some smart bulbs and hubs offer energy monitoring. This feature tracks how much electricity your lights use over time. You can see daily, weekly, or monthly usage in your app. This helps you identify habits that waste energy—like leaving lights on in unused rooms.
Tip: Use energy monitoring to compare usage before and after adding smart bulbs. You might be surprised by how much you’re saving—and how quickly you’ll recoup the initial cost.
Cost vs. Long-Term Savings
Smart bulbs cost more upfront than traditional bulbs—typically $10 to $30 per bulb. But over time, they save you money on two fronts: lower energy bills and longer lifespan.
Upfront Costs
- Smart LED bulb (60W equivalent): $10–$20
- Smart bulb with hub (e.g., Philips Hue): $50–$100 for starter kit
- Smart plug (if bulb doesn’t have built-in controls): $15–$25
Long-Term Savings
A 60W equivalent smart bulb uses about 9 watts. If used 5 hours a day, that’s 1.35 kWh per day, or 405 kWh per year. At $0.12 per kWh, that’s $48.60 in electricity costs per year. Compare that to a 60-watt incandescent bulb: 300 watts used daily = 109.5 kWh/year = $13.14/year. Wait—that math seems off. Let’s correct it:
- 60W incandescent: 300 watts/day = 0.3 kWh/day = 109.5 kWh/year → $13.14/year
- 9W smart LED: 45 watts/day = 0.045 kWh/day = 16.425 kWh/year → $1.97/year
That’s a difference of $11.17 per year in energy costs. Over 10 years, that’s $111.70 in savings—not counting the bulb’s longer lifespan (25,000+ hours vs. 1,000 for incandescent).
Payback Period
At $15 per bulb, it takes about 1.3 years to recoup the cost through energy savings. After that, every year is pure savings. Add in the cost of replacing incandescent bulbs every 1,000 hours (about 1 year of use), and smart bulbs become even more cost-effective.
Tips for Maximizing Energy Efficiency with Smart Bulbs
You can get even more energy savings by using smart bulbs the right way. Here are some practical tips:
- Use dimmers: Dimming reduces energy use and extends bulb life.
- Set schedules: Automate lights to turn off when not needed.
- Install motion sensors: Use in hallways, closets, and garages.
- Leverage geofencing: Turn lights off when you leave home.
- Choose efficient models: Look for ENERGY STAR certified bulbs.
- Group bulbs by room: Create routines for entire rooms, not just one light.
- Monitor usage: Use app reports to track and reduce waste.
ENERGY STAR Certification
Look for bulbs with ENERGY STAR certification. These meet strict efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. ENERGY STAR smart bulbs use at least 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs and last 10 times longer.
Zigbee vs. Wi-Fi: Which Uses Less Energy?
Smart bulbs use different wireless protocols. Wi-Fi bulbs connect directly to your router and use more power. Zigbee bulbs use less energy and work with hubs, making them more efficient for large smart home setups.
Environmental Impact of Smart Bulbs
Beyond energy savings, smart bulbs reduce your environmental footprint in several ways:
- Less waste: Longer lifespan means fewer bulbs in landfills.
- No mercury: Unlike CFLs, LEDs don’t contain toxic mercury.
- Reduced carbon emissions: Lower energy use means less demand on power plants.
- Efficient manufacturing: Modern LED production is cleaner and more sustainable.
By switching to smart bulbs, you’re not just saving money—you’re helping the planet.
Common Misconceptions About Smart Bulbs
Some people worry that smart bulbs use more energy because they’re “connected” or “always on.” But that’s not true. The standby power used by smart bulbs is minimal—usually less than 1 watt. That’s far less than the energy saved by replacing a 60-watt incandescent with a 9-watt smart LED.
Another myth: “Smart bulbs are only for tech lovers.” In reality, they’re simple to use and offer real benefits for everyone—especially those who want to save energy and reduce their bills.
Conclusion: Are Smart Bulbs More Energy Efficient?
Yes, smart bulbs are more energy efficient than traditional incandescent, halogen, and even many CFL bulbs. They use LED technology to consume far less electricity, and their smart features—like scheduling, dimming, and motion detection—help you use light more wisely. While they cost more upfront, the long-term savings on energy bills and replacements make them a smart investment.
To get the most out of your smart bulbs, choose efficient models, use automation wisely, and monitor your energy use. With the right setup, you can enjoy bright, convenient lighting while reducing your environmental impact and saving money.
Whether you’re upgrading your entire home or just one room, smart bulbs are a simple, effective way to make your home smarter and greener.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do smart bulbs use more energy than regular bulbs?
No, smart bulbs typically use less energy than regular incandescent bulbs. Most smart bulbs are LED-based and use 75% to 90% less energy. The “smart” features don’t significantly increase power use—they actually help reduce waste.
Can smart bulbs help reduce my electricity bill?
Yes, smart bulbs can significantly reduce your electricity bill. By using less wattage and being turned off automatically, they lower energy consumption. Over time, the savings often outweigh the higher upfront cost.
Are all smart bulbs energy efficient?
Most smart bulbs are energy efficient because they use LED technology. However, efficiency varies by model. Look for ENERGY STAR certification and check the wattage and lumens to ensure you’re getting a truly efficient bulb.
Do smart bulbs have to be on all the time to save energy?
No, smart bulbs don’t need to be on all the time. In fact, using features like scheduling and motion detection helps you save energy by turning lights off when not needed. Their efficiency comes from smart usage, not constant operation.
Can I use smart bulbs with regular dimmer switches?
Some smart bulbs work with regular dimmer switches, but many require smart dimmers to avoid flickering. Always check the bulb’s compatibility before buying. Using dimming features can save up to 50% more energy.
How long do smart bulbs last compared to traditional bulbs?
Smart LED bulbs last 25,000 to 50,000 hours, while incandescent bulbs last about 1,000 hours. This longer lifespan reduces waste and replacement costs, making smart bulbs more sustainable over time.