Smart bulbs use significantly less electricity than traditional incandescent bulbs, making them an eco-friendly and cost-effective lighting solution. With features like dimming, scheduling, and motion detection, they help you save even more energy by using light only when needed.
Key Takeaways
- Smart bulbs consume far less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs—often 75–80% less—thanks to LED technology.
- Features like dimming and scheduling help reduce electricity usage by up to 50% compared to always-on lighting.
- Energy usage varies by model; always check wattage and look for ENERGY STAR certification for maximum efficiency.
- Standby power consumption from smart bulbs is minimal but can add up—use smart plugs or power strips to cut phantom load.
- Integration with smart home systems like Google Home or Alexa enables automation that further reduces unnecessary usage.
- Over time, smart bulbs save money despite higher upfront costs, especially in high-usage households.
- Environmental impact is lower due to reduced electricity demand and longer lifespan (up to 25,000 hours).
📑 Table of Contents
- Does Smart Bulb Consume Much Electricity?
- How Much Electricity Do Smart Bulbs Use?
- What Makes Smart Bulbs More Efficient?
- Do Smart Bulbs Use Power When Off?
- Are Smart Bulbs Worth the Energy Savings?
- Tips to Maximize Energy Efficiency with Smart Bulbs
- Environmental Impact of Smart Bulbs
- Common Misconceptions About Smart Bulbs and Energy Use
- Conclusion: Are Smart Bulbs a Smart Choice for Energy?
Does Smart Bulb Consume Much Electricity?
You’ve probably seen the glowing, color-changing smart bulbs in tech stores or online ads—and you’ve likely wondered: Do these fancy lights really use more electricity than regular bulbs? The short answer? No, not really. In fact, smart bulbs are often more energy-efficient than traditional lighting options. But let’s dig deeper to understand exactly how much electricity they consume, what makes them different, and how you can use them to save both energy and money.
Smart bulbs are a type of LED bulb that can be controlled remotely via apps, voice assistants, or smart home systems. They come in a variety of colors, brightness levels, and even features like motion detection and scheduling. But beyond the convenience and ambiance they bring, many people are curious about their environmental and financial impact. Are they a green upgrade? Do they really save energy—or are they just another tech gadget that drains your wallet and your electricity?
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about smart bulb energy consumption. From comparing wattage to understanding standby power, we’ll help you make an informed decision about whether smart bulbs are worth the investment—especially when it comes to energy use. Let’s light the way to smarter, more efficient lighting!
How Much Electricity Do Smart Bulbs Use?
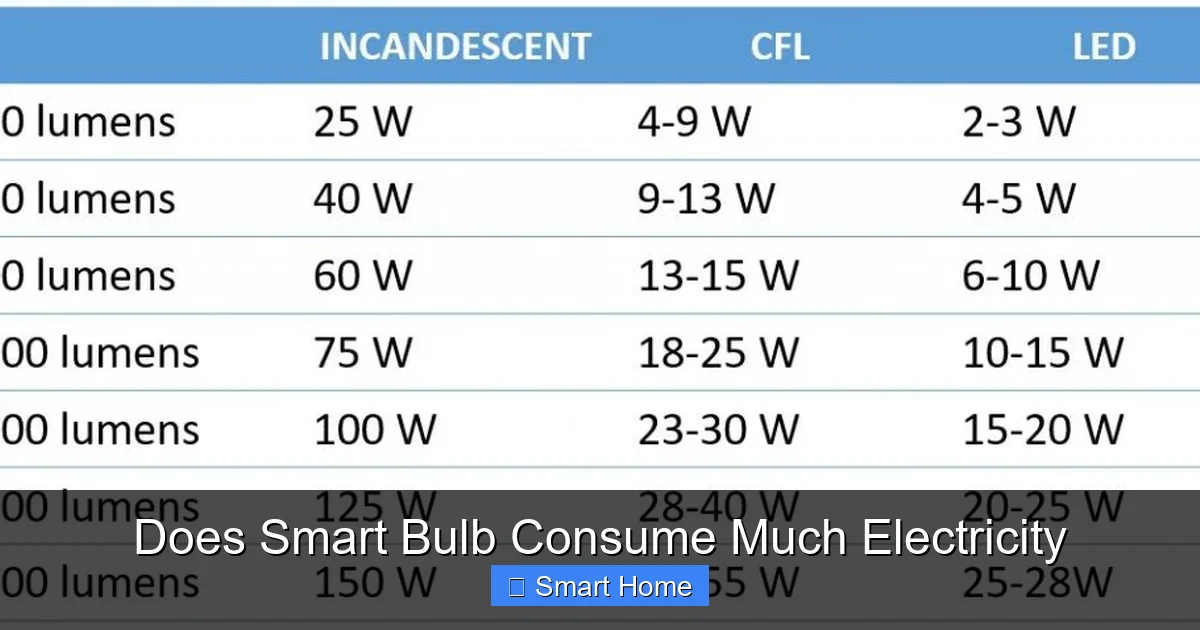
To understand whether smart bulbs consume much electricity, we first need to look at how much energy they actually use. Most smart bulbs are LED-based, and LEDs are known for their energy efficiency. Let’s compare a few common types of bulbs to put things in perspective.
Visual guide about Does Smart Bulb Consume Much Electricity
Image source: effiworkx.com
Comparing Wattage: Smart Bulbs vs. Traditional Bulbs
Here’s a simple comparison of wattage (energy usage) for different bulb types:
- Incandescent bulb (60W): Produces about 800 lumens (brightness), uses 60 watts of electricity.
- Halogen bulb (43W): Slightly more efficient than incandescents, still uses more power for the same brightness.
- Compact fluorescent (CFL) (13–15W): Uses about 80% less energy than incandescents for the same light output.
- LED smart bulb (9–12W): Produces the same 800 lumens using only 9–12 watts—up to 85% less energy than incandescents.
So, even though a smart bulb might use 9 watts, it gives off the same light as a 60-watt incandescent. That means smart bulbs consume far less electricity than older bulb types. For example, if you replace ten 60-watt incandescent bulbs with ten 9-watt smart bulbs, you’re using 510 fewer watts of electricity—just by switching bulbs.
Real-World Energy Consumption Example
Let’s do a quick calculation. Suppose you use one smart bulb for 5 hours a day. At 9 watts, that’s:
9 watts × 5 hours = 45 watt-hours per day
Multiply that by 30 days:
45 × 30 = 1,350 watt-hours = 1.35 kilowatt-hours (kWh)
If your electricity rate is $0.12 per kWh (average in the U.S.), then:
1.35 kWh × $0.12 = $0.162 per month
That’s less than 2 cents a day—or about $5 per year for one bulb. Now, imagine doing that for 20 bulbs in your home. You could save over $100 a year just by switching to smart bulbs.
What Makes Smart Bulbs More Efficient?
You might be thinking, “Okay, but smart bulbs have extra features—sensors, Wi-Fi, apps—so they must use more power, right?” Not necessarily. The key to their efficiency lies in the technology they use and how they’re designed.

Visual guide about Does Smart Bulb Consume Much Electricity
Image source: khabarroundup.com
LED Technology Is the Real Energy Saver
Smart bulbs are almost always LED-based. LEDs convert over 80% of electricity into light, compared to just 10–20% for incandescents. The rest is wasted as heat. LEDs also last much longer—typically 25,000 to 50,000 hours—so you replace them far less often.
Even though smart bulbs have added components like microchips and wireless modules, these don’t significantly increase energy use. In fact, modern smart bulbs are designed to be energy-efficient from the ground up.
Dimming and Scheduling Save Even More Energy
One of the biggest energy savers in smart bulbs is dimming. Lower brightness = less wattage. For example, a 9-watt smart bulb set to 50% brightness uses about 4–5 watts—less than half its full power.
Scheduling is another game-changer. Imagine your living room light turns on at sunset and off at 11 PM automatically. No more lights left on all night. Smart bulbs can be programmed to adjust based on your routine, daylight levels, or even weather.
Motion sensors and geofencing (using your phone’s location) can turn lights on only when needed. So if you’re home, lights stay off; if you leave, they activate. All of this reduces unnecessary usage and saves electricity.
Do Smart Bulbs Use Power When Off?
This is a common concern: “If the bulb is off, is it still using electricity?” The answer is yes—but only a little. This is called standby power or phantom load.
Visual guide about Does Smart Bulb Consume Much Electricity
Image source: effiworkx.com
How Much Standby Power Do Smart Bulbs Use?
Smart bulbs use a tiny amount of power to stay connected to your Wi-Fi network and listen for commands. On average, this is about 0.5 to 1 watt when the bulb is off or in standby mode. That’s not much—but over time, it adds up.
For example, if a smart bulb uses 0.8 watts in standby and is plugged in 24/7:
0.8 watts × 24 hours × 30 days = 57.6 watt-hours = 0.0576 kWh per month
At $0.12 per kWh, that’s about 7 cents a month in standby power. For 20 bulbs, that’s $1.40 a month—or $16.80 a year.
How to Reduce Standby Power
You don’t have to live with standby power. Here’s how to minimize it:
- Use a smart plug with a physical switch. Turn off the plug when not in use (e.g., during long absences).
- Enable sleep mode on your smart bulb app—some allow the bulb to go into ultra-low-power mode.
- Unplug during vacations or when the room is unused for extended periods.
- Choose bulbs with low standby consumption—look for models rated under 0.5 watts when off.
While standby power is real, it’s still a small fraction of total usage. The real savings come from using the bulb intelligently—not from avoiding standby mode.
Are Smart Bulbs Worth the Energy Savings?
Even with standby power, smart bulbs are a net positive for energy efficiency. Let’s compare the total annual cost of different lighting setups.
Annual Electricity Cost Comparison (10 bulbs, 5 hours/day)
| Bulb Type | Wattage | Daily Usage (kWh) | Monthly Cost | Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent (60W) | 60W | 3.0 kWh | $1.08 | $12.96 |
| CFL (13W) | 13W | 0.65 kWh | $0.23 | $2.76 |
| Smart LED (9W) | 9W | 0.45 kWh | $0.16 | $1.92 |
As you can see, smart bulbs cost less than both CFLs and incandescents. And that’s before factoring in longer lifespan and automation benefits.
Long-Term Savings Beyond Electricity
Smart bulbs last 25–30 times longer than incandescent bulbs. So, while they cost more upfront ($10–$25 each), you won’t need to replace them for years. That means fewer trips to the store, less waste, and lower long-term costs.
Plus, the energy savings compound. Over 10 years, switching from incandescents to smart LEDs could save you over $100 in electricity—and reduce your carbon footprint significantly.
Tips to Maximize Energy Efficiency with Smart Bulbs
You can get even more energy savings by using your smart bulbs wisely. Here are practical tips:
Use Scheduling and Automation
Set your lights to turn on only when needed. For example:
- Turn on hallway lights only between 6 PM and 6 AM.
- Use geofencing so lights activate when you arrive home.
- Dim lights at bedtime or when you’re watching TV.
Automation reduces human error—no more leaving lights on in empty rooms.
Take Advantage of Natural Light
Use smart bulbs that integrate with daylight sensors. These bulbs adjust brightness based on how much sunlight is coming through the window. So, if it’s bright outside, the indoor light dims automatically—saving energy.
Group Bulbs and Control Zones
Instead of turning on every light in a room, create lighting zones. For example, use only the ceiling light during the day and turn off desk lamps when not in use. This prevents over-lighting and waste.
Choose High-Efficiency Models
Not all smart bulbs are equal. Look for:
- ENERGY STAR certification
- Low standby power (under 0.5W)
- High lumens per watt (brightness per unit of energy)
- Compatibility with efficient voice assistants (like Google Assistant or Alexa)
Brands like Philips Hue, LIFX, and Wyze offer efficient, well-reviewed options.
Turn Off When Not Needed
Even with automation, remember to turn off lights in rarely used rooms—like guest bathrooms or attics. Smart bulbs make it easy to control from your phone, so there’s no excuse for waste.
Environmental Impact of Smart Bulbs
Beyond cost savings, smart bulbs have a positive environmental impact. Here’s how:
Lower Carbon Footprint
Because they use less electricity, smart bulbs reduce greenhouse gas emissions—especially if your power comes from fossil fuels. A 2020 study by the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) found that replacing incandescent bulbs with LEDs could prevent 34 million tons of carbon emissions annually in the U.S. alone.
Reduced Waste
Smart bulbs last 25,000+ hours—that’s over 20 years with average use. Fewer replacements mean less packaging, less transport, and less landfill waste.
Support for Renewable Energy
As more homes adopt smart lighting, demand for efficient appliances grows—which encourages utilities to invest in renewable energy sources. Efficient lighting is a small but meaningful step toward a greener future.
Common Misconceptions About Smart Bulbs and Energy Use
Let’s clear up some myths:
Myth 1: “Smart bulbs use more power because they’re connected to Wi-Fi.”
False. The Wi-Fi module uses very little power—usually less than 1 watt. The main energy draw comes from the LED itself, which is efficient by design.
Myth 2: “All smart bulbs consume the same amount of electricity.”
Not true. Wattage varies by model. A 12W smart bulb uses more energy than a 9W one. Always check the specs.
Myth 3: “Smart bulbs are only for tech lovers—not for energy savers.”
On the contrary, their automation and scheduling features make them ideal for saving energy. They’re perfect for people who want convenience and efficiency.
Conclusion: Are Smart Bulbs a Smart Choice for Energy?
So, does a smart bulb consume much electricity? Compared to traditional bulbs, no—they consume far less. With wattages typically between 7 and 12 watts, smart bulbs use up to 85% less energy than incandescents while providing the same or better light quality. Their LED technology, combined with features like dimming, scheduling, and motion detection, allows you to use light only when and where you need it.
Yes, smart bulbs do use a small amount of power in standby mode—but this can be minimized with smart plugs or manual off switches. The real energy savings come from intelligent use, not just the bulb itself. Over time, the combination of lower electricity bills, longer lifespan, and reduced environmental impact makes smart bulbs a smart investment for any home.
If you’re looking to cut energy costs and reduce your carbon footprint, smart bulbs are a simple, effective first step. They’re not just trendy—they’re a practical, eco-friendly upgrade that works with your lifestyle. So go ahead: dim the lights, schedule your lighting, and enjoy the savings. Your wallet and the planet will thank you.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many watts does a smart bulb use?
Most smart bulbs use between 7 and 12 watts. For example, a 9-watt smart bulb can replace a 60-watt incandescent while using only a fraction of the energy.
Are smart bulbs more energy-efficient than regular bulbs?
Yes, smart bulbs are typically more efficient because they use LED technology. They use 75–80% less energy than incandescent bulbs and can be dimmed or scheduled to save even more.
Do smart bulbs use electricity when turned off?
Yes, but only a small amount—usually 0.5 to 1 watt—for standby mode. This can be reduced by using smart plugs with physical switches.
Can I save money by using smart bulbs?
Absolutely. Smart bulbs use less electricity and last longer, reducing both energy bills and replacement costs over time. They can save you $50–$100 annually in a typical home.
Are smart bulbs bad for the environment?
No, they’re better for the environment. They use less energy, produce less heat, and have a longer lifespan, reducing waste and carbon emissions.
Should I replace all my bulbs with smart bulbs to save energy?
It’s not necessary, but it helps. Start with frequently used lights (like living rooms or hallways). Even partial upgrades can lead to noticeable energy and cost savings.